Water, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 26 maio 2024
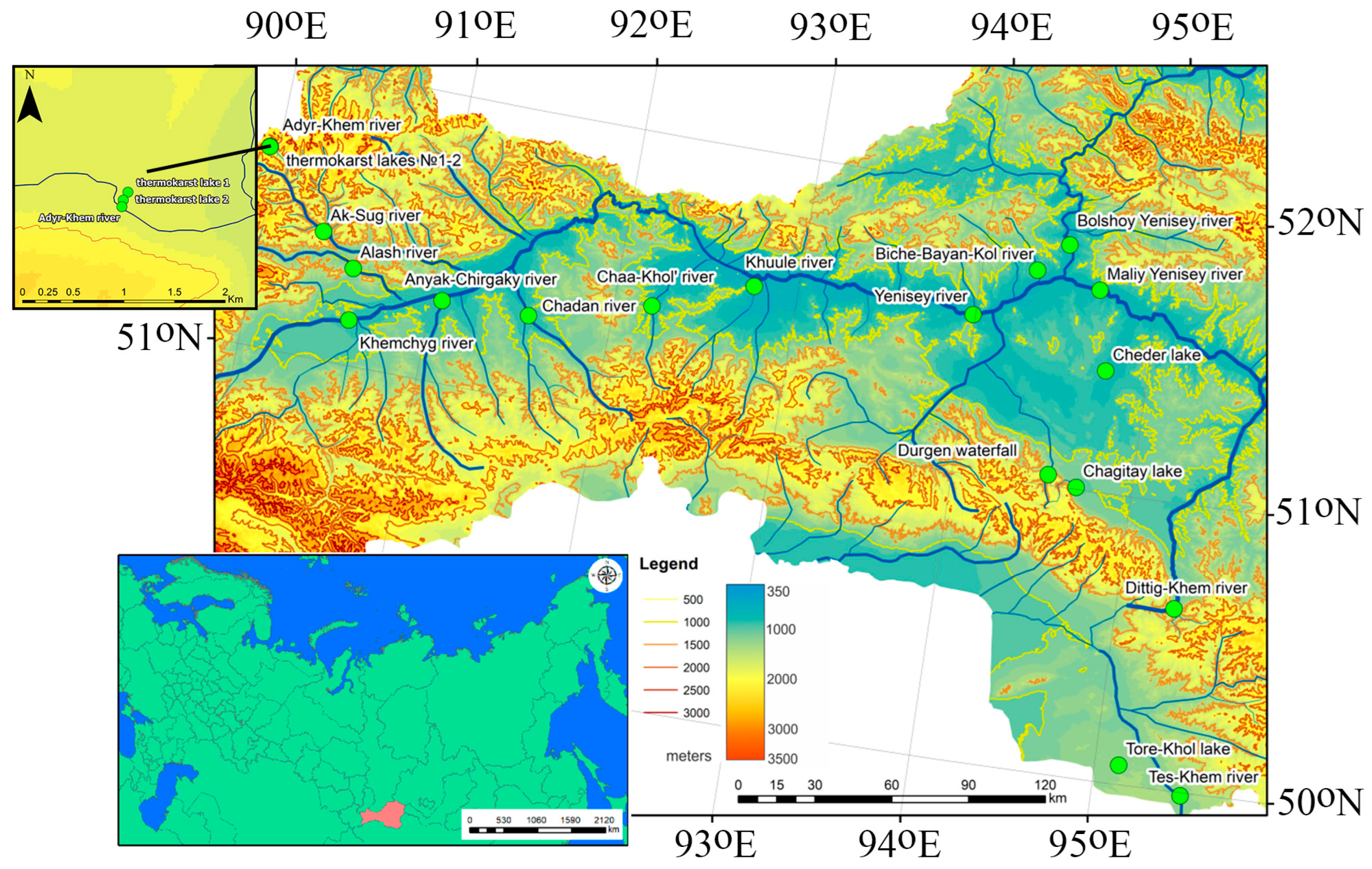
The carbon (C) cycle in inland waters, including carbon concentrations in and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from water surfaces, are at the forefront of biogeochemical studies, especially in regions strongly impacted by ongoing climate change. Towards a better understanding of C storage, transport and emission in Central Asian mountain regions, an area of knowledge that has been extremely poorly studied until now, here, we carried out systematic measurements of dissolved C and CO2 emissions in rivers and lakes located along a macrotransect of various natural landscapes in the Sayan–Altai mountain region, from the high mountains of the Western Sayan in the northwest of Tyva to the arid (dry) steppes and semideserts in the intermountain basins in the southeast of Tyva on the border with Mongolia. New data on major hydrochemical parameters and CO2 fluxes (fCO2) gathered by floating chambers and dissolved organic and inorganic carbon (DOC and DIC, respectively) concentrations collected over the four main hydrological seasons allowed us to assess the current C biogeochemical status of these water bodies in order to judge possible future changes under climate warming. We further tested the impact of permafrost, river watershed size, lake area and climate parameters as well as ‘internal’ biogeochemical drivers (pH, mineralization, organic matter quality and bacterial population) on CO2 concentration and emissions in lakes and rivers of this region and compared them with available data from other subarctic and mountain settings. We found strong environmental control of the CO2 pattern in the studied water bodies, with thermokarst lakes being drastically different from other lakes. In freshwater lakes, pCO2 negatively correlated with O2, whereas the water temperature exerted a positive impact on pCO2 in large rivers. Overall, the large complexity of counteracting external and internal drivers of CO2 exchange between the water surfaces and the atmosphere (CO2-rich underground DIC influx and lateral soil and subsurface water; CO2 production in the water column due to dissolved and particulate OC biodegradation; CO2 uptake by aquatic biota) precluded establishing simple causalities between a single environmental parameter and the fCO2 of rivers and lakes. The season-averaged CO2 emission flux from the rivers of Tyva measured in this study was comparable, with some uncertainty, to the C uptake fluxes from terrestrial ecosystems of the region, which were assessed in other works.

Water Glass Symbols, Pictograms - Empty, Half, Full Glass Of Water

Water‐Assisted and Catalyst‐Free Hetero‐Michael Additions

Policy brief Archives - REACH: Improving water security for the poor

earth, fire, water, sky wild, soft, free and full of flowers.

Family Day at the Lake - City of Graham, NC

Realistic Water Text Effect Mockup Stock Template
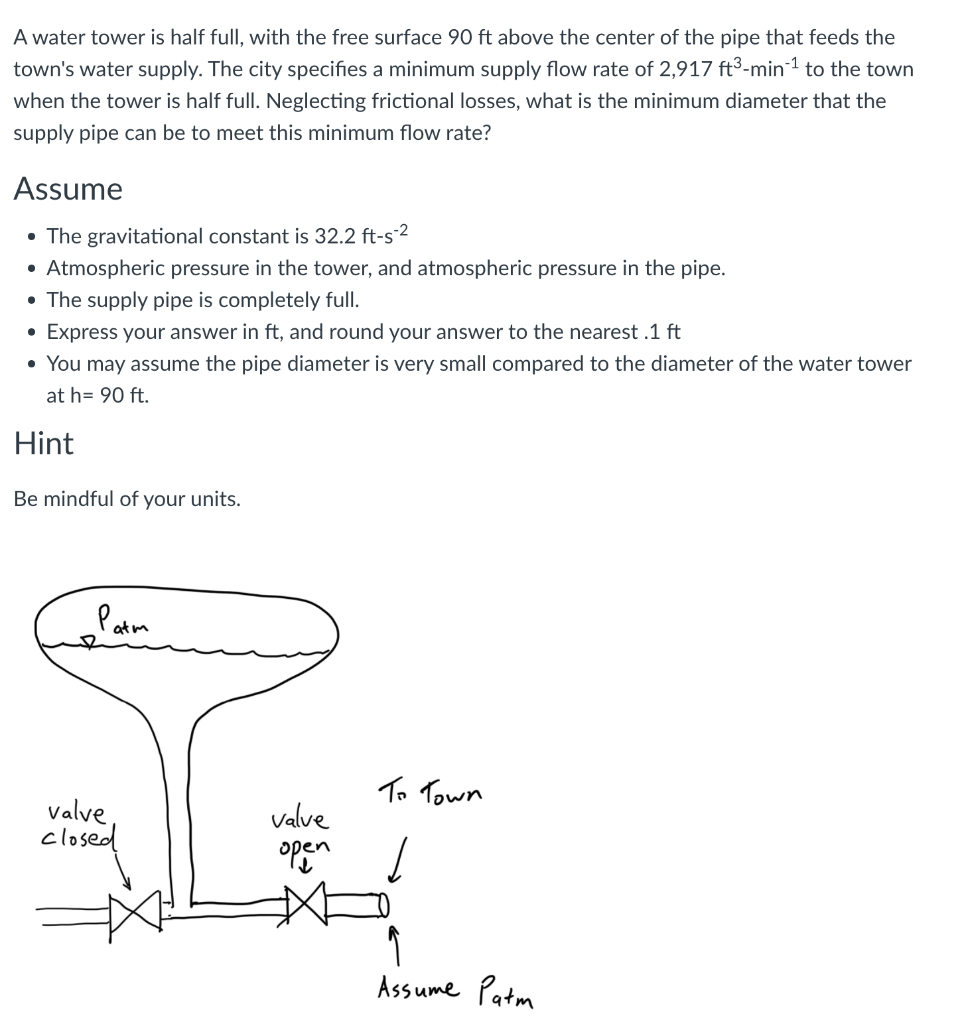
Solved A water tower is half full, with the free surface 90
Characteristics Of Free Water And Bound Water In Foods - Colaboratory

Water Advertising Stock Video Footage for Free Download

Listen Free to How Not to Drown in a Glass of Water: A Novel by

Water Conservation Garden Kids Free Coupon - San Diego Museum Council

Rinse Free Body Wash & Shampoo Hospital Grade Full Hair & Body
Maps of the median water total THM (A), BrTHM (B), and free

Simpure Y7 Reverse Osmosis System Countertop Water Filter

OriginClear and Envirogen to Partner on Water On Demand
Recomendado para você
-
 Underground RP26 maio 2024
Underground RP26 maio 2024 -
![Underground Roleplay [ANDROID E PC] – Discord](https://discord.onl/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/MarcusMaia-150x150.jpg) Underground Roleplay [ANDROID E PC] – Discord26 maio 2024
Underground Roleplay [ANDROID E PC] – Discord26 maio 2024 -
 Forum gratis : UnderG26 maio 2024
Forum gratis : UnderG26 maio 2024 -
 San Andreas Roleplay26 maio 2024
San Andreas Roleplay26 maio 2024 -
samp underground rp|Pesquisa do TikTok26 maio 2024
-
 gta samp rp26 maio 2024
gta samp rp26 maio 2024 -
 PDF) Numerical Study of Gas Breakthrough in Preferential Rocks for Underground Nuclear Waste Repositories26 maio 2024
PDF) Numerical Study of Gas Breakthrough in Preferential Rocks for Underground Nuclear Waste Repositories26 maio 2024 -
CFJV00198B, PDF, Pipe (Fluid Conveyance)26 maio 2024
-
 Paris Metro Map Coffee Mug Paris Mug France Mug Paris26 maio 2024
Paris Metro Map Coffee Mug Paris Mug France Mug Paris26 maio 2024 -
 GTA: More Mods Removed Amidst GTA Remaster Rumors26 maio 2024
GTA: More Mods Removed Amidst GTA Remaster Rumors26 maio 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Hogwarts Legacy Will Have Denuvo; PC Specs Revealed26 maio 2024
Hogwarts Legacy Will Have Denuvo; PC Specs Revealed26 maio 2024 -
 The Judit Polgar interview - News - ChessAnyTime26 maio 2024
The Judit Polgar interview - News - ChessAnyTime26 maio 2024 -
 Escola de Monstros – Aula em Jogo26 maio 2024
Escola de Monstros – Aula em Jogo26 maio 2024 -
Odds explained, PDF, Sports Rules And Regulations26 maio 2024
-
 NoobFeed Game of The Year 202226 maio 2024
NoobFeed Game of The Year 202226 maio 2024 -
 Call Of Duty: Advanced Warfare Artbook - Dan Martin26 maio 2024
Call Of Duty: Advanced Warfare Artbook - Dan Martin26 maio 2024 -
 Roblox Flee The Facility 10 Mystery Items26 maio 2024
Roblox Flee The Facility 10 Mystery Items26 maio 2024 -
 Prime Gaming loot, Fallout Wiki26 maio 2024
Prime Gaming loot, Fallout Wiki26 maio 2024 -
 One Piece HEART OF GOLD Original Mad Treasure Mad Key Chain bonus package26 maio 2024
One Piece HEART OF GOLD Original Mad Treasure Mad Key Chain bonus package26 maio 2024 -
 Robert Rauschenberg - Editions & Works Lot 33 April 202326 maio 2024
Robert Rauschenberg - Editions & Works Lot 33 April 202326 maio 2024


